Indicate which market structure characterizes each firm – Delving into the realm of market structure and firm characteristics, this exploration unveils the intricate relationship between market dynamics and firm behavior. By examining the defining traits of each market structure, we embark on a journey to determine the market structure that characterizes each firm, unlocking insights into their strategic decision-making and implications for consumers.
Through a comprehensive analysis of firm characteristics, we unravel the factors that shape their behavior, such as size, market share, and barriers to entry. By examining real-world examples, we illuminate how market structure influences firm performance, pricing strategies, and consumer welfare, revealing the profound impact of market dynamics on the competitive landscape.
Identify Market Structures
Market structure refers to the characteristics of a market that influence the behavior of firms and consumers. It is determined by factors such as the number of buyers and sellers, the degree of product differentiation, and the barriers to entry and exit.
There are four main types of market structures:
- Perfect competition
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic competition
Perfect Competition
Perfect competition is characterized by a large number of buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, and no barriers to entry or exit. In this type of market, individual firms have no market power and are price takers.
Monopoly
A monopoly is characterized by a single seller with no close substitutes. This gives the monopolist complete market power, allowing it to set prices above marginal cost and earn economic profits.
Oligopoly
An oligopoly is characterized by a small number of large firms that control a significant portion of the market. Oligopolists are interdependent, meaning that their decisions affect the behavior of their rivals.
Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is characterized by a large number of firms selling differentiated products. Firms have some market power due to product differentiation, but entry and exit are relatively easy.
Analyze Firm Characteristics
The characteristics of firms can influence their behavior and the market structure in which they operate. These characteristics include:
- Size
- Market share
- Barriers to entry
Firms that are large and have a significant market share have more market power than smaller firms. Barriers to entry, such as high capital requirements or government regulations, can make it difficult for new firms to enter the market, which can lead to higher prices and lower consumer welfare.
Examples of Firms in Different Market Structures
- Perfect competition:Agricultural markets, such as the market for corn or wheat
- Monopoly:Natural monopolies, such as public utilities or water companies
- Oligopoly:The automobile industry, the telecommunications industry
- Monopolistic competition:The restaurant industry, the clothing industry
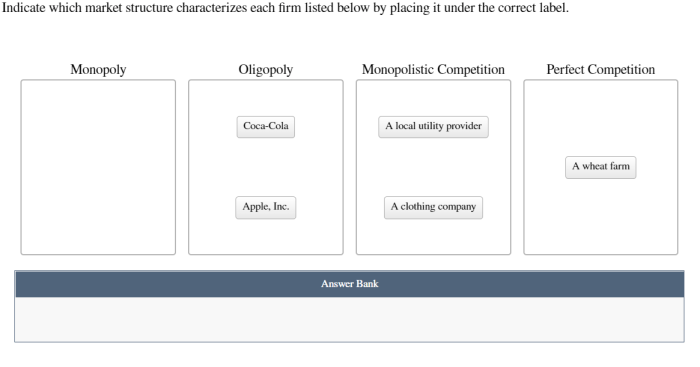
Determine Market Structure of Firms: Indicate Which Market Structure Characterizes Each Firm
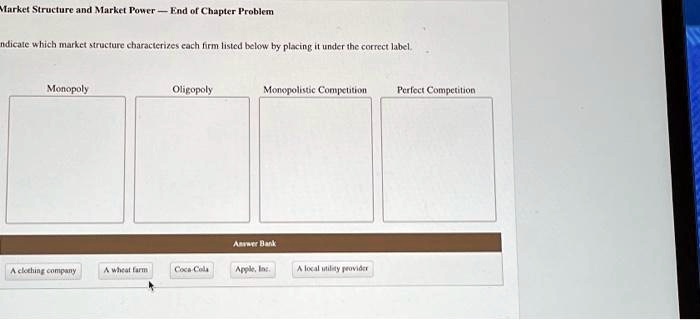
The market structure of a firm can be determined by examining its characteristics. The following table summarizes the key characteristics of each market structure:
| Market Structure | Number of Firms | Product Differentiation | Barriers to Entry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perfect competition | Many | None | None |
| Monopoly | One | None | High |
| Oligopoly | Few | May be present | May be present |
| Monopolistic competition | Many | Present | Low |
Discuss Implications of Market Structure
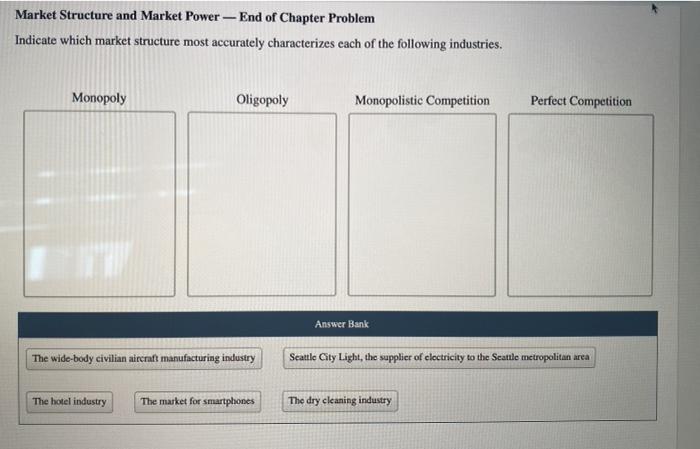
The market structure in which a firm operates has implications for its behavior, pricing strategies, and consumer welfare.
Firm Behavior
In perfect competition, firms are price takers and produce at the point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. In a monopoly, firms have market power and can set prices above marginal cost to maximize profits.
Pricing Strategies
In perfect competition, firms charge a price equal to marginal cost. In a monopoly, firms can charge a price above marginal cost, but they must consider the elasticity of demand.
Consumer Welfare, Indicate which market structure characterizes each firm
Perfect competition leads to the most efficient allocation of resources and the lowest prices for consumers. Monopolies can lead to higher prices and reduced consumer welfare.
Illustrate with Real-World Examples
Perfect competition:The agricultural market is an example of perfect competition. There are many farmers selling a homogeneous product (corn or wheat), and there are no barriers to entry or exit.
Monopoly:Microsoft is an example of a monopoly in the operating system market. It has a dominant market share and high barriers to entry due to its large installed base and network effects.
Oligopoly:The automobile industry is an example of an oligopoly. There are a few large firms that control a significant portion of the market, and there are barriers to entry due to high capital requirements and economies of scale.
Monopolistic competition:The restaurant industry is an example of monopolistic competition. There are many restaurants selling differentiated products, and there are low barriers to entry and exit.
Essential FAQs
What are the key characteristics of perfect competition?
Perfect competition is characterized by numerous small firms, homogeneous products, perfect information, and free entry and exit.
How does market structure influence pricing strategies?
Market structure plays a significant role in determining pricing strategies, with firms in monopolies having greater pricing power than firms in perfectly competitive markets.
What are the implications of market structure for consumer welfare?
Market structure can impact consumer welfare, with highly concentrated markets potentially leading to higher prices and reduced consumer choice.