Delving into the realm of DNA structure and replication POGIL answers, we embark on an enlightening journey that unravels the intricate workings of life’s fundamental building blocks. Through a comprehensive examination of DNA’s molecular composition, double-helix structure, and replication process, we uncover the profound significance of this molecule in shaping the biological world.
POGIL activities provide an interactive and engaging platform for students to explore these concepts, fostering a deeper understanding of DNA’s role in cell division, growth, and the diverse applications that drive advancements in medicine, forensics, and biotechnology.
DNA Structure
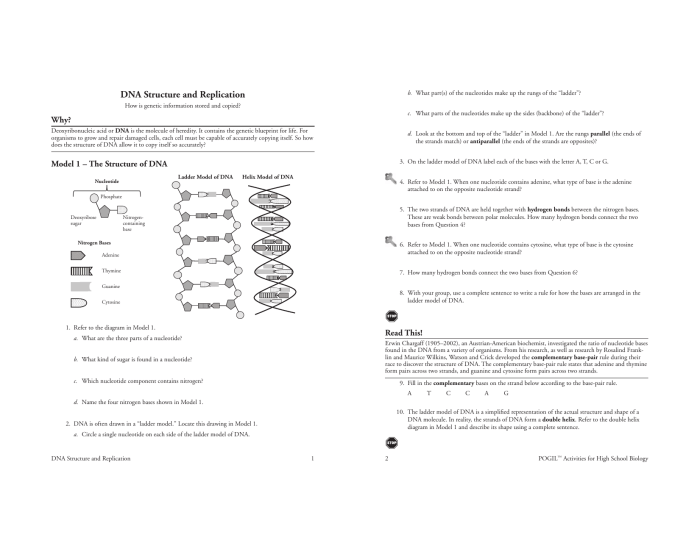
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is found in the nucleus of cells and is made up of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
These nucleotides are arranged in a specific order to form genes, which are the units of heredity.
Components of a DNA Molecule
Each nucleotide in a DNA molecule consists of a deoxyribose sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The deoxyribose sugar molecule forms the backbone of the DNA molecule, while the phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases form the sides of the molecule.
Double-Helix Structure of DNA
DNA molecules are arranged in a double-helix structure. The two strands of the helix are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. Adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine. This pairing of bases is known as complementary base pairing.
Major and Minor Grooves of the DNA Double Helix
The double-helix structure of DNA has two grooves: the major groove and the minor groove. The major groove is wider than the minor groove, and it contains more hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. This makes the major groove more stable than the minor groove.
DNA Replication
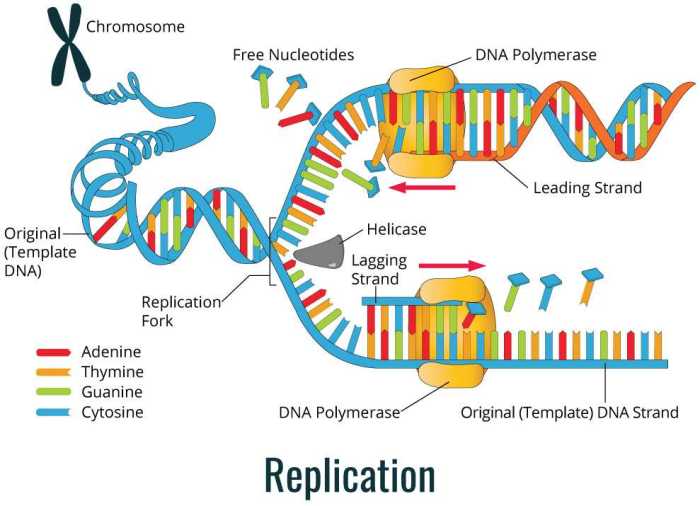
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division and growth. DNA replication begins when the DNA molecule unwinds and the two strands separate. Each strand then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand of DNA.
Role of Helicase, DNA Polymerase, and Ligase, Dna structure and replication pogil answers
The enzyme helicase unwinds the DNA molecule and separates the two strands. The enzyme DNA polymerase then adds new nucleotides to each strand, using the existing strand as a template. The enzyme ligase joins the new nucleotides together to form a continuous strand of DNA.
Leading and Lagging Strands
During DNA replication, one strand of DNA is synthesized continuously, while the other strand is synthesized in short fragments called Okazaki fragments. The strand that is synthesized continuously is called the leading strand, while the strand that is synthesized in fragments is called the lagging strand.
Importance of DNA Replication
DNA replication is essential for cell division and growth. It ensures that each new cell has a complete copy of the DNA from the parent cell. DNA replication is also essential for DNA repair. When DNA is damaged, the cell can use the undamaged strand as a template to repair the damaged strand.
POGIL Activities
POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) activities are a type of active learning activity that helps students learn by doing. POGIL activities related to DNA structure and replication can help students understand these concepts in a more hands-on way.
Benefits of POGIL Activities
POGIL activities can help students:
- Develop a deeper understanding of DNA structure and replication
- Improve their problem-solving skills
- Develop their critical thinking skills
- Work collaboratively with others
Applications of DNA Structure and Replication: Dna Structure And Replication Pogil Answers
DNA structure and replication have a wide range of applications in fields such as medicine, forensics, and biotechnology.
Applications in Medicine
DNA structure and replication are used in a variety of medical applications, including:
- Genetic testing: DNA testing can be used to identify genetic disorders, determine paternity, and diagnose diseases.
- Disease diagnosis: DNA replication can be used to diagnose diseases such as cancer and HIV.
- Gene therapy: Gene therapy involves using DNA to treat diseases by replacing or repairing damaged genes.
Applications in Forensics
DNA structure and replication are used in a variety of forensic applications, including:
- DNA fingerprinting: DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals by comparing their DNA.
- DNA profiling: DNA profiling is a technique used to identify criminals by comparing their DNA to DNA found at crime scenes.
Applications in Biotechnology
DNA structure and replication are used in a variety of biotechnology applications, including:
- Genetic engineering: Genetic engineering involves using DNA to modify the genetic makeup of organisms.
- DNA cloning: DNA cloning is a technique used to create multiple copies of a specific gene or DNA fragment.
- DNA sequencing: DNA sequencing is a technique used to determine the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule.
Query Resolution
What are the key components of a DNA molecule?
Nucleotides, deoxyribose sugar, and phosphate groups
Describe the process of DNA replication.
Involves helicase, DNA polymerase, and ligase, resulting in leading and lagging strands
How do POGIL activities enhance understanding of DNA structure and replication?
Provide interactive simulations, promote critical thinking, and facilitate collaborative learning