Plant and animal adaptations worksheet introduces the fascinating world of adaptations, the remarkable traits and behaviors that organisms have evolved to thrive in their environments. From the waxy leaves of desert plants to the echolocation of bats, adaptations are the key to understanding the diversity and resilience of life on Earth.
This worksheet delves into the structural, functional, and behavioral adaptations of plants and animals, exploring how these traits enhance survival and reproductive success. By examining specific examples and comparing adaptations across different environments, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay between organisms and their surroundings.
Plant Adaptations

Plants have evolved a remarkable array of structural and functional adaptations to survive in diverse environments. These adaptations enhance their ability to acquire resources, withstand challenges, and reproduce successfully.
Structural Adaptations, Plant and animal adaptations worksheet
- Waxy Leaves:Reduce water loss in arid environments.
- Spines:Deter herbivores and protect against water loss.
- CAM Photosynthesis:Enables water conservation in desert plants.
Functional Adaptations
- Symbiotic Relationships:Form mutually beneficial associations with fungi (mycorrhizae) and bacteria (rhizobia).
- Seed Dormancy:Allows seeds to survive unfavorable conditions and germinate when conditions improve.
- Photoperiodism:Respond to changes in day length to regulate growth and flowering.
Animal Adaptations: Plant And Animal Adaptations Worksheet
Animals have developed a wide range of adaptations to cope with diverse challenges in their environments. These adaptations enhance their survival, reproductive success, and ability to exploit specific ecological niches.
Structural Adaptations, Plant and animal adaptations worksheet
- Camouflage:Conceals animals from predators and prey.
- Mimicry:Resembles other organisms for protection.
- Echolocation:Enables navigation and prey detection in darkness.
Behavioral Adaptations
- Migration:Seasonal movement to exploit favorable habitats.
- Hibernation:Energy conservation during winter.
- Social Behavior:Cooperation and communication enhance survival and reproduction.
Adaptations in Different Environments
Plants and animals have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in specific environments:
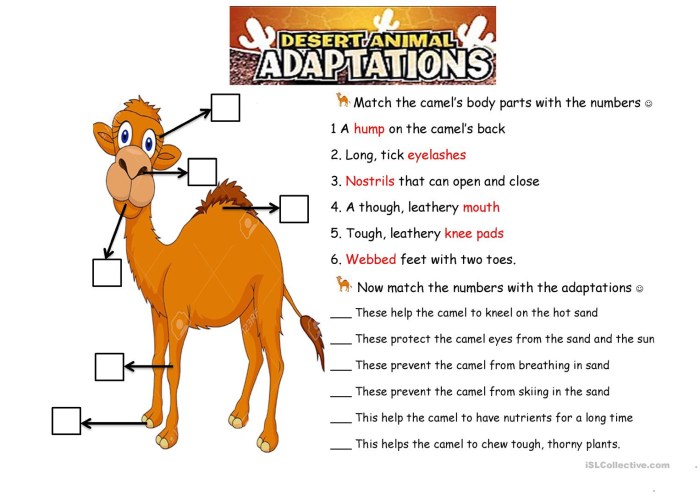
Deserts
- Drought-Tolerant Plants:Waxy leaves, deep roots, and CAM photosynthesis.
- Desert Animals:Nocturnal behavior, burrowing, and water-conserving adaptations.
Rainforests
- Epiphytic Plants:Grow on trees to access sunlight.
- Rainforest Animals:Arboreal adaptations, bright coloration, and camouflage.
Polar Regions
- Cold-Tolerant Plants:Anti-freeze proteins, insulating tissues, and dormancy.
- Polar Animals:Thick fur, blubber, and adaptations for hunting in icy environments.
Comparing Plant and Animal Adaptations
| Adaptation Type | Purpose | Examples | Environmental Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural | Enhance physical characteristics | Waxy leaves, spines, camouflage, echolocation | Protect from harsh conditions, deter predators, and aid in survival |
| Functional | Enhance physiological processes | CAM photosynthesis, seed dormancy, hibernation, social behavior | Regulate growth, reproduction, and energy conservation |
| Behavioral | Enhance interactions with the environment | Migration, burrowing, communication, mimicry | Increase survival, reproductive success, and resource utilization |
Evolution and Adaptations
Natural selection drives the evolution of plant and animal adaptations. Environmental pressures select for traits that enhance survival and reproductive success.
Over time, specific adaptations have evolved in response to environmental challenges, contributing to the survival and diversification of species:
- Peppered Moths:Industrial pollution favored dark-colored moths, demonstrating rapid adaptation.
- Antibiotic Resistance:Bacteria have evolved resistance to antibiotics due to selective pressure.
- Drug Resistance:Cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy, highlighting the ongoing evolutionary process.
Questions and Answers
What is the difference between plant and animal adaptations?
Plant adaptations are primarily structural and functional, enabling them to absorb sunlight, water, and nutrients from their environment. Animal adaptations, on the other hand, include both physical and behavioral traits that enhance survival, such as camouflage, mimicry, and hunting strategies.
How do adaptations contribute to the survival of organisms?
Adaptations increase an organism’s fitness within its environment by enhancing its ability to obtain resources, avoid predators, and reproduce successfully. For example, waxy leaves in desert plants reduce water loss, while camouflage in animals helps them evade detection.
How does natural selection drive the evolution of adaptations?
Natural selection favors individuals with traits that increase their survival and reproductive success. Over time, these traits become more common in the population, leading to the evolution of adaptations that are well-suited to the specific environmental challenges faced by the organism.
